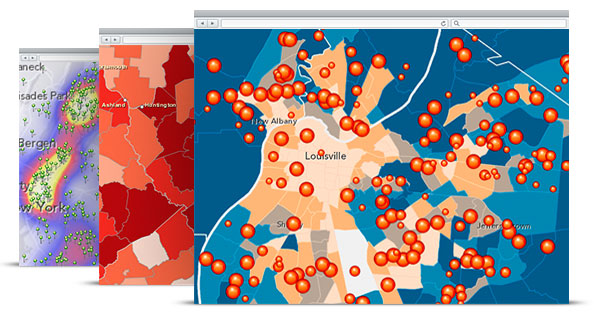
You’ve probably heard of location analysis. But what exactly is it and why do we need it? We will look at Esri’s interactive mapping software, the handbook they recently published on location analysis, and explore the four main imperatives. We’ll also touch on the importance of data for location analysis. Read on to learn more. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Esri Location Analytics
When a company needs to understand their supply chain, location analytics is the answer. Esri Location Analytics helps organizations unlock the geographic context of their business systems. Global supply chains have become truly global, with a typhoon in Asia impacting business in Europe. In addition, the demands of North America drive global manufacturing performance. The use of GIS and location analytics helps companies improve visibility and reduce risk, while data integration balances production with demand.
With Esri Location Analytics, businesses can combine their huge amounts of data to uncover hidden patterns and trends. These insights can also help them improve their customer engagement and relationship management efforts.
The Esri Spatial Business Initiative fosters collaboration between business leaders and GIS experts, including students, through special events and programs. The initiative’s annual research conference seeks to advance spatial business and build a network of location-based businesses. It also sponsors executive retreats and workshops for leaders in the private sector. These events are designed to equip students with the necessary skills to apply this technology in the workplace. The event will include speakers from Esri, thrdPlace, and the private sector.
Esri’s interactive mapping software
When it comes to location analytics, Esri has several tools to make it easier for business professionals to visualize data. Its dynamic mapping software combines powerful analytical tools with map styles and a comprehensive data library. Esri apps make it easy to customize maps to suit your audience. They can be embedded in websites and distributed across an organization. Each one is designed to serve a specific purpose. The Esri Maps for Office software add-in is available as a free download for Microsoft Office 2010.
For those who don’t need a lot of data manipulation, Tableau Public is a good option. This tool features an easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface that recommends the best way to display your data. It can even create maps for you, allowing you to publish them on the web with a public URL. Tableau is free for teachers and students, but it’s priced at $70 per month for individual users.
ArcGIS Online is a hosted version of ArcGIS, which provides secure, simple access to maps and apps. Its license varies by location, but the Esri online version includes Esri’s desktop GIS ArcGIS Pro. Users can also create applications and web maps using ArcGIS Online. For desktop use, there’s also a Windows desktop GIS called ArcGIS Desktop. The software allows you to create 3D models of objects with ArcGIS CityEngine.
Esri’s recent handbook on-location analysis
If you’re looking to learn the basics of GIS with a practical approach, you’ll be glad to hear that Esri’s recent handbook on ArcGIS Pro 2.8 contains a chapter on location analytics. This book is a practical guide that covers the basic concepts of location analysis and introduces the technology behind it. It is an excellent choice for students or self-learners with no prior GIS experience. Regardless of your current level of GIS knowledge, you’ll finish this book with confidence and knowledge to use ArcGIS Pro on your own.
The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis is divided into three volumes, each covering different techniques. Volume 3 focuses on using modeling techniques in GIS analyses. In this chapter, author Andy Mitchell outlines how to use GIS to make better decisions. Volume four explains how to use GIS to make spatial measurements and identify patterns. This chapter is especially useful for those who work in the public sector and need to use the data in a more comprehensive manner.
The second edition of Esri’s handbook on-location analysis provides a more comprehensive guide. The first chapter provides a foundational introduction to GIS and explains the basics of location analysis. It also includes several online lessons to help students gain more practical experience.
The four imperatives of location analysis
In a world where data is often cluttered, ignoring retail location analysis software may cost your company valuable opportunities. Inadequate access to spatial tools has been a big barrier to decision-makers. However, Esri Location Analytics provides a transparent GIS-to-business system interface. This enables decision-makers to leverage data from multiple sources and gain insights from a location. By applying the four imperatives of location analytics, you can unlock greater value in your data.
The McWorld dynamic is a product of four imperatives: information-technology, ecological, and resource. These four imperatives are reshaping the world, decreasing the salience of national borders, and destroying nationalism. In the process of depoliticizing, bureaucratizing, and commercializing the world, the emergence of global capitalism, transnationalism, and decolonization put the movement toward McWorld in a tight competition with forces of national dissolution and centrifugal corruption.